Our solar system, a truly amazing place, holds many wonders, and among them, the planet Mars stands out. It is the fourth planet from the sun, a celestial body that has captured our collective imagination for a very long time. In fact, it's one of the most explored places in our cosmic neighborhood, and, you know, it's the only planet where we have sent special vehicles, like rovers, to truly get a feel for its unusual surface. Scientists and space enthusiasts alike are always looking to learn more about this intriguing world, which, in some respects, seems both familiar and yet quite alien to us here on Earth.
Understanding the actual distances between our home planet and Mars is, in a way, incredibly important. This knowledge is not just for curiosity's sake; it's absolutely crucial for those who plan missions to visit the Red Planet. Whether we are thinking about sending more robotic explorers or even considering future human trips, knowing the typical separation, how it changes, and how long it takes for signals to travel is, well, pretty much everything. It helps us figure out how much fuel we need, how long a trip might take, and even when the best times are to launch a spacecraft. This information, you see, guides a great deal of the work that goes into space travel.
The distance separating Mars and Earth is not a fixed number, which, to be honest, might surprise some people. It shifts quite a bit depending on where both planets are in their paths around the sun. This cosmic dance means that sometimes Mars is relatively close to us, and at other times, it's very, very far away. This variability has a big impact on everything from how bright Mars appears in our night sky to the sheer length of time it takes for a message, or even a spacecraft, to make the trip between the two worlds. It's a dynamic situation, really, and quite fascinating to consider.
- Is Frank Fritz Of American Pickers Dead Unraveling The Truth Behind The Rumors
- Exploring The Life And Career Of Murphy Actor A Comprehensive Guide
- John Nettles A Deep Dive Into The Life And Career Of The Acclaimed Actor
- Are Moon And Tiko Back Together In 2024 The Latest Update On Their Relationship
- Exploring Sex Positive Movies A Deep Dive Into Telugu Cinema On Movierulz
Table of Contents
- What Makes Mars So Special?
- A World of Contrasts - Beyond the Red Hue
- Why Does the Mars Earth Average Distance Matter for Exploration?
- How Far Is Mars - The Numbers Behind the Mars Earth Average Distance
- Understanding Orbital Dance and Mars Earth Average Distance Changes
- What Does the Mars Earth Average Distance Mean for Travel Time?
- Observing the Red Planet - How Mars Earth Average Distance Affects Our View
- The Quest for Life - Driven by Mars Earth Average Distance Insights
What Makes Mars So Special?
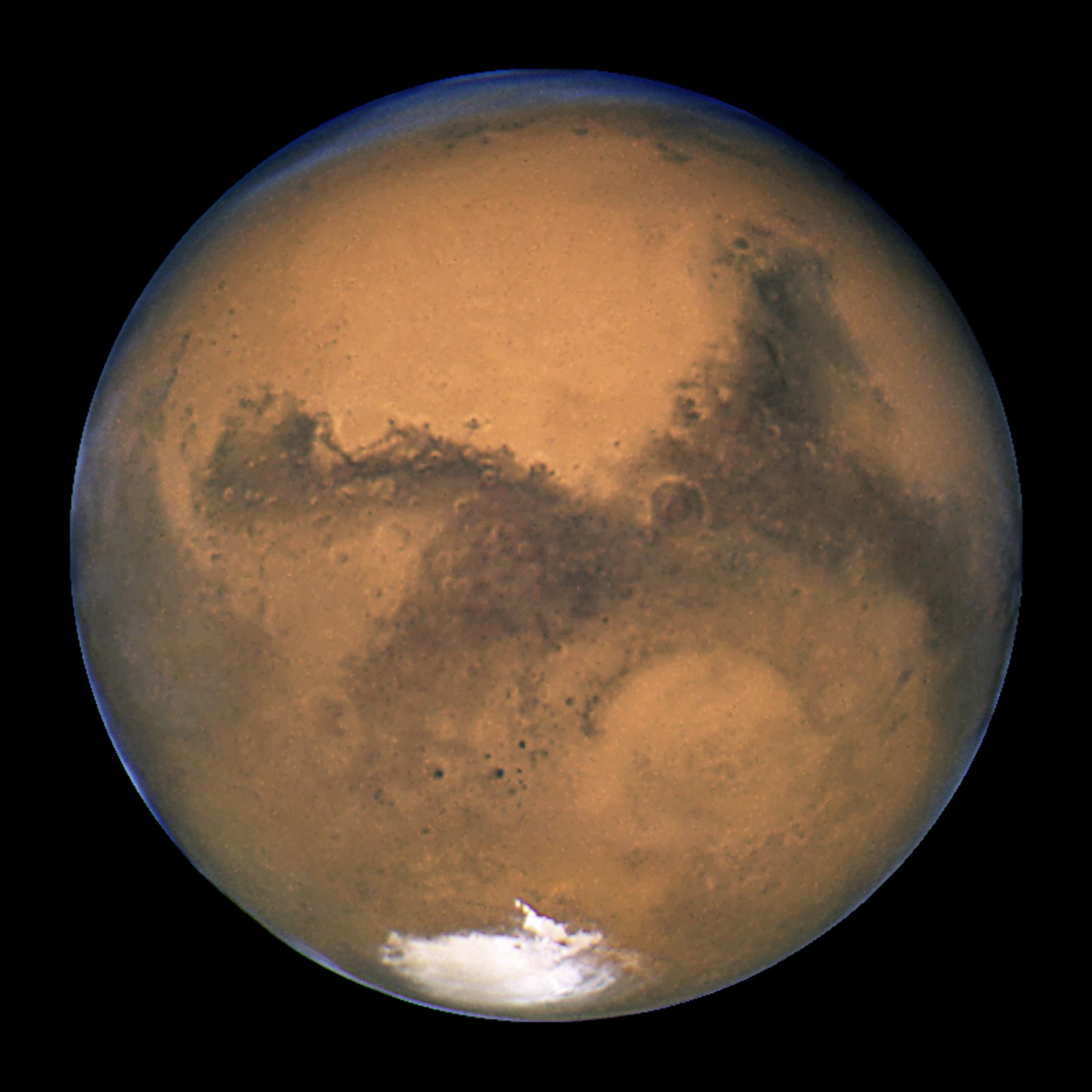
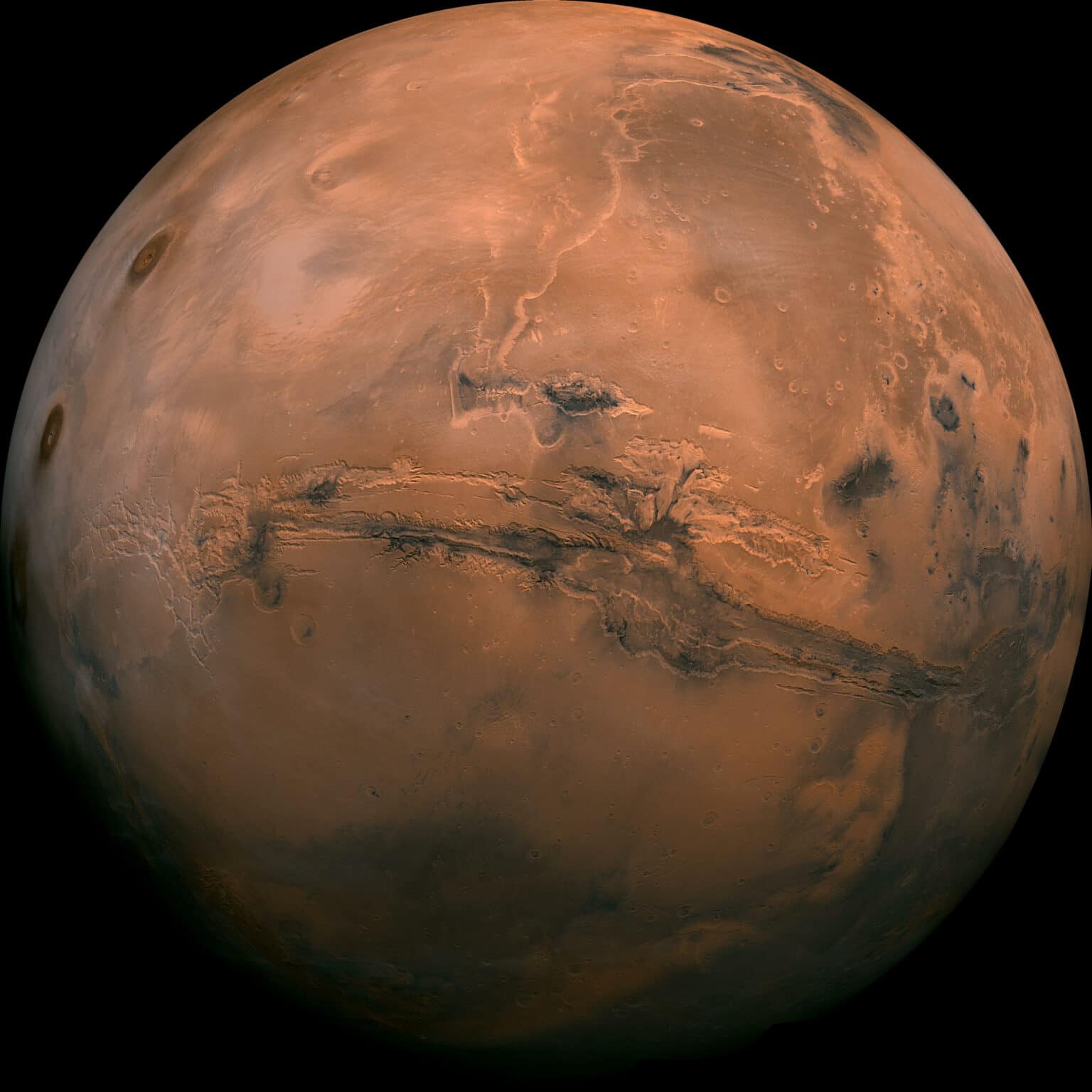
Mars is, as we know, the fourth planet outward from the sun, and it holds a unique spot in our solar system's lineup. It's not the biggest planet; actually, it's the seventh in terms of its overall size and its total mass. Yet, it truly captures our attention. This particular world, named after the ancient Roman god of conflict, has, for a very long time, been seen as a notable reddish mark in the night sky. Its distinctive rusty red appearance is something that sets it apart from the other planets we can easily see. This reddish color, you might say, is a kind of visual story of past events, hinting at a history that involved a lot of change and, perhaps, some destructive forces.
The appeal of Mars goes beyond just its color, though. It's a world that shows us a lot of interesting features. For instance, it has seasons, much like Earth, which is a pretty cool detail. It also has icy caps at its poles, something we often associate with our own planet. Beyond that, we know there are ancient, no-longer-active volcanoes scattered across its surface, along with deep, winding canyons. These features, along with its two rather unusual moons, Phobos and Deimos, paint a picture of a planet with a rich and varied geography. NASA's missions, in particular, have been instrumental in showing us so much about this place, uncovering lots of details about its surface and what lies beneath. In fact, these missions have found a great deal of fascinating information, really helping us piece together the puzzle of this neighboring world.
A World of Contrasts - Beyond the Red Hue
Even though Mars appears so vibrant and active with its seasons and canyons, it is, in reality, a rather cold, dry place, a desert world within our solar system. This current state, however, is not the whole story. There is a lot of information suggesting that, at some point in the distant past, Mars actually had flowing water. This possibility means that Mars might be holding many secrets, especially concerning its earlier days. Scientists are, in fact, working hard to figure out how Mars changed from whatever it was before into the chilly, arid desert world we observe today. This transformation is a significant part of its history, and understanding it helps us learn more about how planets develop and change over incredibly long stretches of time.
- Lyudmila Aleksandrovna Ocheretnaya A Comprehensive Biography
- John Allman The Rock Singer Who Redefined An Era
- Frank From American Pickers Passed Away A Tribute To His Legacy
- Teddy Swims Height Everything You Need To Know
- Frank Fritz Is He Still Alive
The quest to understand Mars's past is, for many, a way to look for signs of life, either from long ago or even still existing today. For example, a robotic explorer recently collected a sample from a fresh area on Mars. This spot had features that could, just possibly, show us if the ground below the surface of Mars once offered an environment that was suitable for living things. This kind of work is truly important because it helps us explore the planet's history and search for proof of life that might have been there in the past, or, you know, perhaps even something that continues to exist now. The core to making sense of Mars, whether we are talking about its past, its present, or even what its future might hold, lies in these ongoing investigations and the data they bring back to us. It is, in a way, a continuous effort to piece together a very old story.
Why Does the Mars Earth Average Distance Matter for Exploration?
The average separation between Earth and Mars is a subject that truly captures the interest of people working in astronomy and those involved in space exploration. Knowing this distance, you see, is not just a piece of trivia; it's absolutely vital for making plans for missions. When we consider sending anything, whether it's a small probe or a larger spacecraft, from our planet to Mars, the distance directly impacts how long the journey will take. For example, if you could travel the shortest distance between Earth and Mars at a typical car speed, say 60 miles per hour, it would take a very, very long time indeed – about 66.5 years to reach Mars! This thought experiment, while not how space travel works, really helps illustrate the vastness of the distances involved and why the exact figures matter so much for practical planning.
Furthermore, the way light and radio waves travel across this vast expanse is also directly tied to the mars earth average distance. The sun's light, which bounces off the surface of Mars, needs a certain amount of time to reach our eyes here on Earth. When our planet is closest to Mars, that light might take around three minutes to get here. However, when Mars is at a more typical separation, that travel time stretches out to about 12 minutes. And if Mars is at its furthest point from us, that light can take as long as 22 minutes to make the journey. These timings are not just for looking at Mars; they are also crucial for communicating with our rovers and spacecraft on its surface. When we send a command, or when a rover sends back data, that signal travels at the speed of light, and the time delay is directly proportional to the distance. So, knowing the mars earth average distance helps us account for these communication delays, which is pretty important for controlling complex machinery millions of miles away.
How Far Is Mars - The Numbers Behind the Mars Earth Average Distance
The distance between Earth and Mars is, as we have touched upon, not a single, unchanging number. It varies quite a lot, depending on where each planet is in its path around the sun. For instance, the furthest apart the two planets will be is about 250 million miles. However, when we talk about the average, or typical, separation between Earth and Mars, it is generally considered to be around 140 million miles. Another way to look at it, using a slightly different measurement, is that Mars orbits roughly 142 million miles, which is about 229 million kilometers, away from Earth. These figures, you know, give us a sense of the vastness of the space between us.
Historical records show us that the minimum distance between Earth and Mars has been as close as 54.6 million kilometers. On the other hand, the maximum distance recorded has stretched out to 401.4 million kilometers. This huge range in distances, which is really quite a lot of difference, happens because of the way the planets move along their orbital paths. The specific distance at any given moment changes based on the respective positions of both planets as they travel around the sun. This means that, for example, the current distance of Mars from Earth might be something like 297,101,762 kilometers, which is roughly equivalent to 1.986003 astronomical units. For this particular separation, light would take about 16 minutes and 31.0248 seconds to travel between the two worlds. These numbers, you see, highlight just how dynamic the planetary system truly is.
When scientists talk about distances in our solar system, they often use a unit called the Astronomical Unit, or AU. This unit, which is the average distance between Earth and the sun, is the most common way for researchers to measure distances in our solar system. So, for example, Mars orbits at an average distance to the sun of about 1.5 AU. This gives us a good sense of its position relative to our star. To put things in perspective, Mercury, which is closer to the sun, is, on average, about 1 AU away from Earth, which is the same as the Earth-Sun distance. This comparison helps illustrate that Mars, on average, is quite a bit further out than Mercury when viewed from Earth. And speaking of other celestial bodies, Ceres, the closest dwarf planet to the sun and the only one in the inner solar system, orbits the sun from an average distance of 257 million miles, which is about 413 million kilometers. That means Ceres is approximately 2.8 times farther from the sun than Earth is. These various measurements, you know, help us map out our cosmic neighborhood.
Understanding Orbital Dance and Mars Earth Average Distance Changes
The changing separation between Earth and Mars is a direct result of their individual journeys around the sun. Each planet follows its own path, and these paths are not perfectly circular; they are more like stretched circles. This means that sometimes, as Earth and Mars move along their respective orbits, they come closer to each other, and at other times, they drift much further apart. The greatest separation occurs when the two planets are on opposite sides of the sun. This arrangement is sometimes referred to as a "Mars conjunction." During these times, Mars is, well, very, very far away from us, making it a less ideal time for missions or even for simply observing the planet clearly.
On the other hand, the closest approach happens when Earth and Mars are in a more direct alignment, almost in a straight line on the same side of the sun. This is when the distance shrinks to its minimum. The huge amount of difference in the distances between the planets really depends on their position on their orbit path. For instance, Mars takes about two Earth years to complete just one orbit around the sun. This longer orbital period, compared to Earth's one-year trip, means that the alignments for closest approaches don't happen every year. This orbital mechanics, you see, is why the mars earth average distance is just that—an average—and not a constant figure. It's a rather intricate cosmic dance that constantly shifts the view and the travel possibilities between our two worlds.
What Does the Mars Earth Average Distance Mean for Travel Time?
The time it takes for anything to travel between Earth and Mars is, quite naturally, heavily influenced by the mars earth average distance. We know that radio waves, which are used for communication with spacecraft, travel at an incredible speed, approximately 3.0 × 10^5 kilometers per second. So, if we consider the average separation of 2.25 × 10^8 kilometers, which is about 225 million kilometers, we can figure out, on average, how many seconds it takes for a radio signal to make the trip. This calculation is, you know, a fundamental part of mission control. It means that when scientists send a command to a rover on Mars, they have to wait for that signal to cross the vast distance, and then wait again for the rover's response to travel back. This delay means that controlling a rover on Mars is not like driving a remote-control car in your backyard; it requires careful planning and patience due to the significant time lag.
Even though Mars is occasionally the closest planet to Earth after Venus, it is, on average, much further away than either Mercury or Venus. This greater average separation means that missions to Mars typically take longer to reach their destination compared to missions to our other inner planetary neighbors. The travel time is not just about the raw distance, but also about the precise orbital paths taken to conserve fuel and energy. So, while we can calculate the theoretical light travel time, the actual journey for a spacecraft involves complex trajectories that account for the relative speeds and positions of both planets. This is why understanding the mars earth average distance, and its variations, is so absolutely crucial for figuring out how long a trip to the Red Planet will truly take.
Observing the Red Planet - How Mars Earth Average Distance Affects Our View
The changing separation between Earth and Mars also has a direct impact on how we see the Red Planet from our vantage point. When Mars is closest to Earth, it appears quite bright and large in our night sky. This is when its apparent diameter, or how big it looks to us, can reach its maximum, around 25.6 seconds of arc. However, as the mars earth average distance increases and the planets move further apart, Mars looks smaller and less bright. This is why, you know, astronomers and space enthusiasts often wait for those special times when Mars makes a close approach to get the best views through telescopes or even with the unaided eye. The visibility of Mars, therefore, is not constant; it changes with its position relative to Earth.
This variability in appearance is a clear illustration of how the orbital paths of the planets influence our observations. When Mars is farthest away, perhaps during a "Mars conjunction" where it is on the opposite side of the sun from us, it can be quite challenging to observe. The light reflecting from its surface has to travel a much greater distance, and the planet itself appears much smaller in the sky. So, for anyone wanting to get a good look at our planetary neighbor, keeping track of the current distance of Mars with a reliable and accurate tracker is quite helpful. This allows observers to know when the conditions are most favorable for viewing, making the most of those moments when the mars earth average distance shrinks to its more favorable ranges for observation.
The Quest for Life - Driven by Mars Earth Average Distance Insights
Our ongoing efforts to explore Mars are deeply connected to the desire to understand its history and to search for evidence of past, or even present, life. The insights we gain about the planet's characteristics, like its cold, desert nature today, and the suggestions that it once had flowing water, are all pieces of a larger puzzle. Scientists are continuously uncovering how Mars transformed into the dry world it is now. This quest for knowledge is, in a way, driven by the hope that Mars might hold clues about how life begins and adapts, perhaps even offering insights into the possibilities of life beyond Earth. The missions we send, the samples we collect, and the data we analyze are all part of this grand investigation, and the distance between our planets plays a role in how we conduct these studies.
The very fact that we can send rovers and probes to Mars, and that we can communicate with them, relies fundamentally on our precise understanding of the mars earth average distance and its variations. This knowledge allows us to plan when to send missions, ensuring they arrive at the most opportune times. It also helps us manage the significant communication delays that arise from the vast separation. The information we gather from these missions, like the recent sample drilled from a region that might reveal if Mars's subsurface once supported life, contributes to our overall comprehension of the planet. This continuous exploration, guided by our understanding of planetary distances, helps us piece together the story of Mars and its potential for life, which is, you know, one of the most compelling questions we can ask about our place in the universe.
Related Resources:
- Lyudmila Aleksandrovna Ocheretnaya A Comprehensive Biography
- John Allman The Rise Of A Talented Singer
- Air Astana 2024 Incident Engine Video Analysis And Insights
- Tiko And Moon Back Together A Journey Of Love And Reconciliation
- Exploring The Cinematic Journey Of Dhruv Vikram A Comprehensive Guide To His Movies

Detail Author:
- Name : Dr. Shannon Wehner
- Username : nfeil
- Email : delphia.stamm@gmail.com
- Birthdate : 1996-04-21
- Address : 98420 Gulgowski Parkway New Lurabury, MA 02596-0195
- Phone : 1-779-710-7899
- Company : Sauer, Runolfsson and Keebler
- Job : Housekeeper
- Bio : Veritatis doloremque deserunt sed assumenda. Quasi excepturi doloremque illum eos. Voluptatibus fuga velit officia reprehenderit veniam tenetur deleniti non. Et non rerum dicta et ex.
Socials
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/johnson2015
- username : johnson2015
- bio : Et et sunt ut laborum. Totam totam dolorum quo.
- followers : 164
- following : 1476
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@rjohnson
- username : rjohnson
- bio : Sed autem nemo necessitatibus esse a voluptatibus.
- followers : 5754
- following : 2183
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/rogers_official
- username : rogers_official
- bio : Est quis aut accusantium praesentium voluptatum voluptatem culpa.
- followers : 3089
- following : 2378